Electrical equipment is a significant cause of structural fires in industrial facilities, and heating is often the cause of structural fires in manufacturing units. Excessive heating linked to high resistance or extreme current flow leads to most electrical systems errors. Infrared Thermography, which uses an infra-red camera to detect hot/ cold areas on a segment, helps identify the normally invisible thermal anomalies that may cause a failure ahead of the actual failure.
Growth in automation and the internet of things (IoT) has led to the bourgeoning use of electrical systems in all sectors. Therefore, monitoring the health of electrical systems has become even more critical than before.
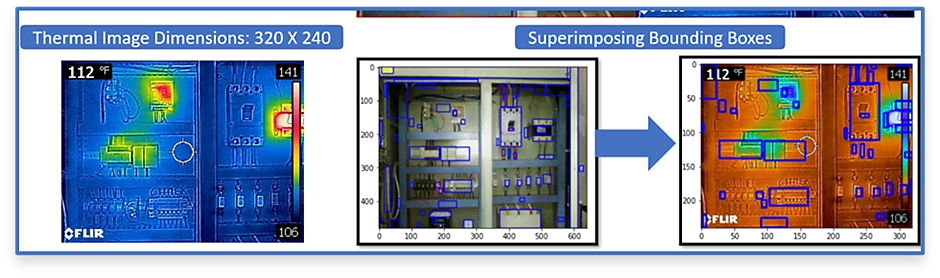
Thermal imaging is a powerful remote sensing technique that can monitor all types of electrical equipment in a manufacturing environment. Thermal imaging analysis can avoid accidents, reduce downtime, and eventually lead to safer sites/plants and cost savings. It is used in diverse industries such as Oil and Gas, Paper and Pulp, Mining, Aerospace, Medical Devices, and others to monitor the health of electrical systems.
In this study, the team captured thermal Images using Infrared cameras like FLIR through non-contact methods. This approach was quicker and did not require any downtime for the machinery.
Currently, Thermal imaging in an electrical system is primarily required to find the equipment's temperature profile. However, this comes with lags in spotting issues in the systems.
A group of researchers studied the application of thermal image analysis with the help of Computer Vision and Deep Learning methods. The aim was to capture deep insights into the thermal image for specific electrical equipment to predict failure rates and provide recommendations for preventive maintenance. Preventive maintenance and intervention can avoid dangerous overheating, resulting in fires that negatively impact personnel safety and productivity.
The researchers collected Thermal images of various electrical panels at the customer's facilities. Then they analysed them over time and compared them to previous thermal images. The team used various web-based computational applications to analyse data and build an ML model that could automate image analysis for the study.
The researchers designed and developed a Deep Learning model using AI and ML concepts to compare the images in 15 seconds versus the manual comparison, a method that relied on human expertise and took on an average of 12 mins per analysis. The project's results recommend extending to several other industrial applications in the manufacturing sector and suggest more frequent monitoring for real-time analysis.
References:
Sastry VVSS, Sangem P.M., Reddy P.V.C., Veluri S, Bandi S., 'AI-based failure prediction of Industrial Electrical Systems using Thermal Imaging,' 2021




